top of page

Tips for printing with flexible filaments
Printing flexible filaments is unfortunately not quite as straight forward as just standard PLA or ABS. Especially on the first couple of tries.
Here are couple of tips and tricks for better results:
Flex Filament types and general tips
A critical parameter when choosing your filament is its stiffness. The more flexible it is the more issues you can expect.
Keep an eye out for a specification usually referred to as Shore Hardness.Most filament makers will list that in their specs for their flexible filaments. Our Flex for example is categorized as Shore 45D which is roughly equivalent to common rubber shoe soles. The larger that number the harder the material.
The Shore Hardness also has to scales: A & D, with A being typically softer. Wikipedia has a great article if you want to know more.
Once you have chosen your filament type it comes down to the right physical and slicer software setup for successful prints.
A couple of general basic tips to start off are:
-
Print much slower than usual:20% of your normal speed is usually working quite well (10-30mm/s depending on your extruder design, more info below)
-
Turn off retraction:Fast back and forward movements will increase the chance of filaments slips, especially on Bowden systems
-
Increase Temperature:In case you have problems increase the temperature in 5 degree steps to reduce nozzle back-pressure
Extruder design specific tips
The next set of consideration depends on your printer design. In general there are two types of extruder designs:
-
Direct Drive Extruderslike used on most RepRap Style printers
-
Bowden Extruders mostly used by Ultimaker type of printers and some other designs based on it
Direct Drive Design considerations
Most user having direct drive extruders have no major problems. The key there is that there are no major gaps between the drive wheel and the hot-end entry where the flexible filament can start to bend.
Have a look at the following direct drive examples:
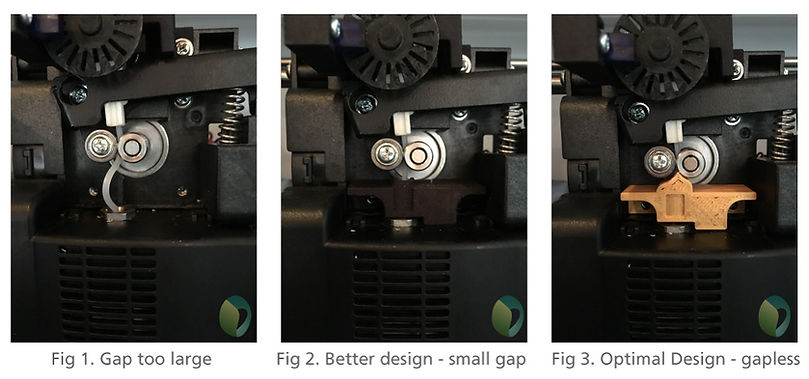
You can clearly see the gap in figure 1. The resistance of the melt zone will cause the filament to start buckling and the transport will fail quickly.
In figure 2 and 3, the distance the filament travels unsupported has been reduced. Both of these are valid designs for successful flex printing.
One of our testbed printers, the original Prusa i3’s design is also fantastic for flexible prints. Together with the provided slicer settings that were optimized for Flex printing we always get fantastic results.
Bowden Design considerations
When it comes to Bowden extruders it becomes more difficult. The Bowden tubes employed are usually quite a bit larger in diameter than the filament itself. That will cause filament potentially buckling in the Bowden tube which increases the resistance a lot. This will lead to the extruder driver slipping and no filament being transported.
There are a few things that are critical for Bowden design extruders:
-
Retractions are an absolute no-no: The fast retraction moves of the compressed filament part in the Bowden tube will yield terrible results.
-
A perfect grip at the point where the hobbed-bolt drive forwards the filament is essential. This typically is adjustable like found here for example on the Ultimaker 2 series
-
The speed should be even further reduced compared to direct drive designs
There is one more trick for tricky problems on Bowden systems: Coating the filament slightly with silicon oil. A couple of drops (not too much) applied on egress to the Bowden tube will great reduce friction and has led to great results for some people.
We for example used our Filament Cleaner Blocks to coat the test filament just so slightly.
bottom of page
